
Creatine Dosage Guide: From Beginner to Expert Results
Share
How Creatine Actually Works In Your Muscles

To really get the most out of your creatine dosage, it helps to know what's going on inside your body. Think of your muscles as a busy factory full of powerful machinery. This machinery needs a very specific type of fuel to perform quick, demanding jobs like sprinting or lifting heavy weights. This high-octane fuel is a molecule called Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
The catch is, your muscles only keep a small amount of ATP on hand—enough for just a few seconds of all-out effort. It's like having a tiny, super-powered battery that dies almost immediately. Once that battery is drained, your factory’s production line grinds to a halt. This is where creatine steps in, acting like a rapid-recharging station for this essential power source.
When you take a creatine supplement, it travels to your muscles and is stored as phosphocreatine. This molecule is basically an energy reserve waiting to be called upon. After a tough set depletes your ATP, phosphocreatine quickly donates its phosphate group to the "used" energy molecule, instantly turning it back into fresh, usable ATP.
This rapid recycling process allows your muscular factory to keep chugging along at full speed for longer. It's what helps you push out that extra one or two reps that are so important for stimulating muscle growth and strength gains.
The Science of Muscle Saturation
Your body does make some creatine on its own, and you get more from foods like red meat and fish. However, for people who are active, these natural levels are rarely enough to completely fill up your muscles' "tanks." Supplementing with creatine helps you top off your reserves, much like filling your car's fuel tank before a long road trip.
Decades of research have shown us the best ways to do this. A well-established method involves a loading phase of 20 grams per day for about five days. This can increase your muscle creatine stores by around 20%. After loading, you switch to a smaller maintenance dose. The extensive research behind these protocols shows just how effective they are.
This increased storage does more than just fuel your workouts. It also pulls more water into the muscle cells in a process known as cellular hydration. This can give your muscles a fuller, more "pumped" appearance and may even help kickstart the biological pathways that build new protein. Learning about this mechanism alongside general muscle building strategies can give you a more complete picture of how to reach your goals.
Ultimately, by keeping your creatine levels high, you create the ideal internal environment for better performance, faster recovery between sets, and long-term muscle growth. The right dosage makes sure your factory is always ready for peak production.
Loading Phase vs. Steady Dosing: Which Path Works Better?
When starting with creatine, think of it like filling up a swimming pool. You have two main options: you can blast it full with a fire hose for a few hours, or you can use a steady garden hose that runs all day. The loading phase is the fire hose, designed to rapidly saturate your muscles. In contrast, steady dosing is the garden hose—a slower, more gradual approach that gets you to the same destination over time. Neither path is universally "better"; the right choice depends on your goals, patience, and how your body responds.
The Loading Phase: Maximum Speed, Potential Bumps
The loading phase is an aggressive strategy built for speed. The standard protocol involves taking a significantly higher amount, usually 20 grams per day, for about 5-7 days. To make this manageable, it's typically split into four 5-gram servings throughout the day. The main advantage is how quickly you can max out your muscle's creatine stores, often leading to noticeable performance and strength gains in about a week.
However, this fast-track method isn't without potential issues. Some individuals report mild digestive discomfort, such as bloating or an upset stomach, when taking such high doses. This happens because creatine pulls water into your muscle cells, and a sudden high intake can disrupt your system. For competitive athletes with an upcoming event or anyone eager to see results quickly, the loading phase is a very effective option.
The Steady Dosing Method: A Gentler, Consistent Climb
The steady dosing approach skips the high-intake week altogether. Instead, you simply start with the standard maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day. This method is much gentler on the digestive system and simpler to follow—just one serving a day. Think of it as making a small, consistent daily investment in your performance.
While you will reach full muscle saturation this way, it takes longer—usually around 3 to 4 weeks compared to one week with loading. The trade-off for this slower timeline is convenience and a lower risk of side effects. For those focused on long-term consistency over immediate impact, or for anyone with a sensitive stomach, steady dosing is often the preferred path.
To help you decide, the table below breaks down the key differences between these two popular strategies.
| Dosing Strategy | Daily Amount | Duration to Saturation | Potential Side Effects | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loading Phase | 20 grams (split into 4 doses) | 5-7 days | Higher chance of bloating, stomach discomfort | Athletes needing quick results, impatient beginners |
| Steady Dosing | 3-5 grams | 3-4 weeks | Minimal to none | Long-term users, individuals with sensitive stomachs |
Ultimately, both strategies lead to the same peak: fully saturated muscles ready to perform. The choice simply comes down to personal preference.
The infographic below shows the kind of results you can expect once your muscles are fully saturated, regardless of which method you choose.
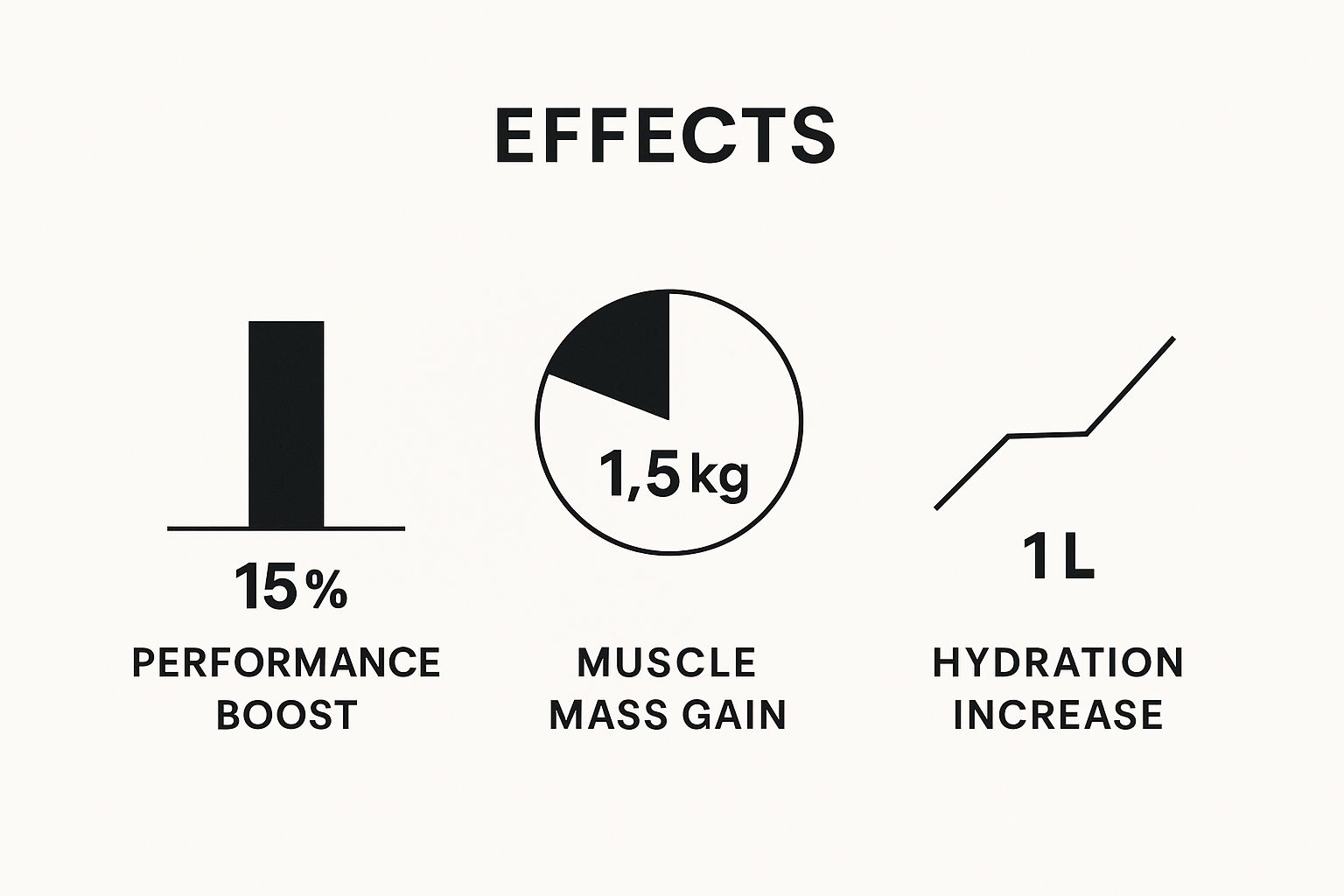
These figures show that the end result of either dosing strategy is enhanced performance and muscle growth. If you want faster results and don't mind a more intensive first week, loading is for you. If you prefer a simpler, gentler approach and are patient, steady dosing is a perfect fit.
Calculating Your Perfect Creatine Dosage

The standard "one-size-fits-all" 5-gram scoop is a common recommendation, but your ideal creatine dosage isn't set in stone. Think of it like fueling a vehicle; a large truck needs more fuel than a small car. Similarly, someone with more muscle mass generally needs more creatine to fully saturate their stores. Tailoring your intake to your body is crucial for getting the best results.
Imagine you're watering plants. You wouldn't give a small succulent the same amount of water as a large oak tree. Your muscles work the same way. Their capacity to hold creatine is directly related to their size. This is why a more precise calculation based on your body weight is often better than a generic dose, ensuring your muscles get exactly what they need.
A More Precise, Body Weight-Based Calculation
For those who want to be more exact, the scientific standard for creatine intake is based on body mass. This approach ensures you supply enough creatine to fill your muscle stores quickly and efficiently, especially during a loading phase. Seminal research established a guideline that remains a gold standard: a creatine loading dose of approximately 0.3 grams per kilogram of body weight per day.
For a 70 kg (154 lb) individual, this works out to about 21 grams daily during the initial loading week, usually split into smaller doses throughout the day. You can explore more on these evidence-based strategies in a fact sheet from the Australian Institute of Sport.
Once your muscles are saturated, you can switch to a maintenance dose. A more personalized maintenance dose is around 0.1 grams per kilogram of body mass per day, which is more specific than the typical 3-5 grams and helps sustain peak performance levels.
Responders vs. Non-Responders: Are You Getting the Full Effect?
An important piece of the puzzle is your individual reaction to creatine. The majority of people are considered "creatine responders," meaning their bodies absorb and use supplemental creatine effectively, leading to clear gains in strength and output. However, a small portion of the population are "non-responders."
This isn't a fault; it often means their natural creatine levels are already high, perhaps due to genetics or a diet rich in red meat. If you’ve been taking creatine correctly for over a month without seeing any difference, you might be in this group. Fortunately, most people do experience significant benefits. Dosing can also vary between different groups of people; to learn more, check out our complete guide to creatine benefits for women. Understanding these personal differences allows you to adjust your strategy for the best possible outcome.
Timing Strategies That Maximize Absorption

While consistent daily intake is the most critical piece of the puzzle, optimizing when you take your creatine dosage can give you a small but meaningful advantage. Think of your muscles as a busy port. Deliveries can arrive at any time, but during peak hours, the dock workers are ready and can unload cargo much faster. For your muscles, these peak hours often revolve around your workouts and meals.
This efficiency boost is largely thanks to a key hormone: insulin. When you eat carbohydrates or protein, your body releases insulin to help move nutrients from your blood into your cells. Taking your creatine with a meal or shake that prompts an insulin response is like giving it an express pass directly into your muscle cells. This is the simple science behind the long-standing tip to mix creatine with grape juice—the sugars trigger an insulin spike, helping to transport the creatine more effectively.
The Post-Workout Window: Your Best Bet
For years, experienced athletes have sworn by the post-workout window, and modern research largely supports this practice. After a demanding training session, your muscles are like depleted sponges, exceptionally ready to soak up nutrients for recovery and growth. Taking creatine within an hour or two after your workout, ideally with a combination of fast-digesting carbs and protein, can notably improve its absorption. This strategy not only helps restock your energy stores faster but also jump-starts the muscle repair process.
While the post-workout period is often seen as the best time, the difference isn't a game-changer. Consistency is always the most important factor. If taking creatine after your workout doesn't fit your schedule, taking it before your workout or with any other meal is still very effective. The main idea is to pair your creatine dose with food to use that insulin-assisted delivery system.
To help you decide what works best for your routine, this table breaks down the most common timing strategies.
| Timing Strategy | When to Take | With What | Expected Benefits | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Workout | Within 1-2 hours after exercise | A shake or meal with protein and carbohydrates | Maximizes muscle uptake when they are most receptive | Athletes and gym-goers looking to optimize recovery and growth. |
| Pre-Workout | 30-60 minutes before exercise | Water or a pre-workout drink | Ensures creatine is readily available during the workout | Individuals who want to feel the performance effects during training. |
| With a Meal | Alongside any substantial meal (breakfast, lunch, etc.) | A balanced meal containing carbs and protein | Uses food-induced insulin spike for better absorption | Anyone seeking a simple, consistent routine that is easy to remember. |
| Anytime | Whenever is most convenient during the day | A glass of water or your favorite beverage | Focuses on maintaining saturated muscle stores | People prioritizing consistency and convenience over minor timing benefits. |
As you can see, the "best" time is flexible and depends on your personal goals and lifestyle. The key takeaway is that pairing creatine with food, especially carbs and protein, is more important than the specific time of day.
Spacing Doses During a Loading Phase
If you choose to do a loading phase, timing becomes a practical necessity to avoid digestive discomfort and ensure your body can handle the higher amount. Consuming 20 grams of creatine in one sitting is often a recipe for an upset stomach. Instead, the best approach is to split this daily total into four smaller, 5-gram servings throughout the day.
A common and effective schedule might look like this:
- Morning: One 5-gram serving with your breakfast.
- Mid-day: A second 5-gram serving with your lunch.
- Post-Workout: A third 5-gram serving with your recovery shake.
- Evening: The final 5-gram serving with your dinner.
This spaced-out method maintains a steady supply of creatine for your muscles and is much easier on your digestive system. It allows your muscles to gradually absorb the supplement without being overwhelmed. Whether you're using a powder or another form, this principle holds true. If you're looking for a convenient, mess-free option for on-the-go servings, you might find our guide comparing creatine gummies vs. powder useful. Ultimately, smart timing helps turn every gram of your creatine into realized potential.
Dosing Mistakes That Kill Your Results
Even the most disciplined training program can be weakened by simple supplementation errors. When it comes to creatine, small mistakes can be the difference between seeing real progress and feeling like you’re spinning your wheels. Just like following a recipe but missing a key ingredient, an incorrect creatine dosage or poor routine can kill your results. Let's break down the most common pitfalls that can trip up even experienced athletes.
Chasing More Than You Need
One of the most frequent errors comes from a "more is better" mindset. After the initial loading phase, some people stick with high doses, assuming it will speed up their gains. But once your muscles are saturated with creatine, they simply can't store any more.
Think of your muscles as a sponge. Once the sponge is full, any extra water just runs off. In the same way, any excess creatine your body can't absorb is simply flushed out. Taking more than the recommended 3-5 grams for maintenance won't lead to better results, but it can open the door to unwanted side effects.
- Wasted Money: You are literally flushing your expensive supplement down the toilet.
- Potential Discomfort: Higher-than-needed doses are more likely to cause stomach bloating or digestive issues.
Sticking to the science-backed maintenance dose is not only more effective but also gentler on your body and your wallet.
Forgetting That Consistency Is King
Another major mistake is inconsistent use. It's easy to be diligent for the first few weeks, but then life gets in the way. People start missing days—especially non-training days—thinking creatine is only necessary on workout days. This is a critical misunderstanding of how creatine functions.
The goal of creatine supplementation is to keep your muscle stores completely full at all times, not just when you hit the gym. It's like keeping a car's fuel tank topped off; you don't wait until it’s empty to refuel. When you skip doses, your muscle creatine levels begin to drop, reducing its effectiveness when you need it most. For the best results, taking your maintenance dose every single day is essential.
Overlooking The Basics
Finally, some users ignore the simple, foundational habits that help creatine work its best. These basics are often the missing link between good and great results.
- Hydration: Creatine works by pulling water into your muscle cells. If you aren't drinking enough water, you not only limit its effect but also risk dehydration and cramping.
- Timing with Food: While not absolutely required, taking creatine with a meal containing carbohydrates and protein can boost absorption. This is because the meal triggers an insulin response from your body, which can help shuttle the creatine into your muscles more efficiently.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you ensure that every gram of creatine you take contributes directly to your strength and performance goals, preventing you from accidentally sabotaging your own hard work.
Creatine Dosage For Women, Beginners, And Older Adults
A standard creatine protocol works well for many, but it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. Think of it like a training plan—you wouldn't give the same workout to a professional athlete and a complete novice. The ideal creatine dosage should account for unique factors like age, sex, and training experience, which all influence how your body responds. Let's look at how to adjust your approach for different groups.
Dosing Considerations for Women
For a long time, creatine was seen as a supplement mainly for male athletes. However, a growing body of research shows its specific advantages for women. Hormonal shifts during the menstrual cycle can affect a woman's natural creatine production, and studies suggest that supplementing can be especially helpful for keeping strength and energy levels stable.
The standard 3-5 gram daily maintenance dose is effective for most women aiming to boost performance and support muscle tone. Because women often have different body compositions and hormonal profiles than men, some may find that a dose on the lower end of that range works perfectly. The key is to find what feels right for your body and aligns with your fitness goals.
A Beginner’s Guide to Starting Creatine
If you're new to creatine, the amount of information out there can feel like a lot to take in. The most important thing to remember is that creatine is a tool to enhance your training, not a replacement for it. It can help you push harder and lift heavier, but the real results come from pairing it with consistent, challenging workouts.
Recent 2025 research reinforces that creatine isn't a magic pill. A study revealed that people who exercised less than the recommended 150 minutes per week saw no meaningful increase in lean muscle from taking 5 grams of creatine daily over 12 weeks compared to a placebo. This shows that a proper creatine dosage needs a solid training stimulus to build muscle. You can read more on these findings about creatine and exercise from UNSW.
For beginners, a straightforward approach is usually best:
- Start with a steady dose: You can skip the loading phase and begin with 3-5 grams per day. This method is gentler on your system and simpler to follow.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. This helps creatine work effectively and can prevent side effects like bloating.
- Be patient: It can take up to four weeks to notice the full effects, so consistency is crucial.
Creatine for Older Adults: Protecting Muscle Mass
As we get older, we naturally start to lose muscle mass and strength in a process called sarcopenia. This decline can affect mobility, balance, and overall quality of life. Research shows that creatine supplementation, especially when combined with resistance training, can be a powerful tool for older adults to fight this process.
For this group, a daily dose of 3-5 grams is recommended. The aim isn't just about building bigger muscles but about preserving the strength needed for everyday life. By helping to maintain muscle power, creatine can support daily activities, from carrying groceries to playing with grandchildren, acting as a valuable partner in promoting healthy aging and independence. For an easy and tasty way to stay consistent, check out our guide on creatine gummies.
Your Complete Creatine Dosage Action Plan
Now it's time to put all that science into practice. We've covered loading phases, maintenance doses, and timing strategies, but what brings it all together is a clear, personalized roadmap. A solid plan is what turns supplementation into real gains, whether you're a competitive athlete tracking every gram or a busy professional just trying to get more from your gym time. This is your blueprint for seeing tangible results in strength and performance from your creatine dosage.
Step 1: Choose Your Starting Strategy
Your first decision is how to kick things off. This isn't about a "right" or "wrong" choice; it's about what best fits your lifestyle, patience, and goals.
- The Fast Track (Loading Phase): If you want to feel the performance benefits as quickly as possible—often within a single week—this is the path for you. It's an excellent choice for athletes with an upcoming event or anyone who is simply eager to see results fast.
- The Steady Path (Maintenance Dose): If you prefer a simpler approach or have a sensitive stomach, this is the way to go. It's a gentler method that helps you avoid potential side effects like bloating and is incredibly easy to maintain long-term.
Think of it like this: both paths lead to the same destination of fully saturated muscles. The loading phase is the express train that gets you there in about one week, while the steady path is the scenic route, taking roughly four weeks.
Step 2: Calculate Your Personalized Dose
While the standard 5-gram scoop is a reliable starting point for many, tailoring the dose to your body weight adds a layer of precision.
- Loading Dose: If you're on the fast track, your daily target is 0.3 grams of creatine per kilogram of your body weight. For someone weighing 75 kg (165 lbs), this comes out to 22.5 grams per day. You'll want to split this into 4-5 smaller doses throughout the day to make it easier on your system.
- Maintenance Dose: For the long haul, a daily intake of 3-5 grams is the gold standard for most people. If you want to be more specific, you can calculate it as 0.1 grams per kilogram of body weight. That same 75 kg person would take 7.5 grams daily—a bit higher than the standard recommendation, but perfectly tailored to their body mass.
Step 3: Build Your Daily Routine
This is where the magic really happens. Consistency is the most critical factor for creatine to work effectively. Your goal is to keep your muscle stores topped off, which means taking it every single day, even on your rest days.
- Integrate with a Meal or Shake: To boost absorption, take your creatine with carbohydrates and protein. This pairing triggers a natural insulin response that helps shuttle the creatine directly into your muscles more efficiently. The post-workout window is a popular and effective time, but honestly, any meal will get the job done.
- Stay Hydrated: Creatine works by pulling water into your muscle cells. Because of this, it's essential to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration supports creatine's function and helps prevent any potential for cramping or dehydration.
By following this straightforward, three-step action plan, you can build a routine that is both sustainable and effective. It eliminates the guesswork and helps ensure your investment in creatine translates directly into better performance, stronger lifts, and faster progress.
Ready to put this plan into action without the mess of powders? Smash.com offers the perfect solution with our delicious, high-potency creatine gummies. Each serving delivers the recommended 5 grams of pure creatine monohydrate, making it easy to stay consistent and smash your goals, wherever you are.