
what is creatine monohydrate: Benefits, Uses & Safety
Share
Let's get right to it. So, what is creatine monohydrate? Think of it as a natural power bank for your muscle cells. It helps your body rapidly produce energy, especially during short, intense bursts of effort like lifting weights or sprinting.
A Deeper Look into Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate is, without a doubt, the most researched and trusted sports supplement out there. It’s celebrated for its proven ability to boost strength, power, and muscle growth. And no, it’s not a steroid or some synthetic lab creation—your body actually makes its own creatine in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. You can also get it from foods like red meat and fish.
The "monohydrate" part just describes its chemical structure: one molecule of creatine attached to one molecule of water. This simple design makes it incredibly stable and easy for your body to absorb and put to work. Its simplicity is its greatest strength.
Why is it So Popular?
Creatine’s popularity isn't just gym-floor gossip; it's built on a mountain of scientific evidence. We're talking about hundreds of studies that confirm it works and is safe to use. That solid research is why everyone from professional athletes to weekend warriors has made it a staple.
Creatine monohydrate stands out because it delivers real, measurable results. It directly fuels your body’s ATP-PC energy system—the go-to source for quick, explosive movements. In the gym, this means squeezing out an extra rep or two or sprinting just a little bit faster.
The demand for this supplement tells the same story. The creatine market was valued at $514.4 million in 2024, and the monohydrate form alone is expected to reach $865.7 million by 2034. That kind of growth is fueled by well-documented benefits and an affordable price point. You can discover more insights about the creatine market and its future trends.
To give you a clear snapshot of what we're talking about, here’s a quick summary of creatine monohydrate’s core attributes.
Creatine Monohydrate At a Glance
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Rapidly replenishes ATP (energy) for muscle contractions. |
| Main Benefits | Increases strength, enhances power output, and supports muscle growth. |
| Scientific Backing | The most studied sports supplement with a strong safety profile. |
| Best For | High-intensity activities like weightlifting, sprinting, and HIIT. |
| Standard Dose | 3-5 grams per day for maintenance. |
This table gives you the essentials, but now we'll dig into the science behind how it actually works its magic in your body.
How Creatine Actually Fuels Your Muscles
To really get what creatine monohydrate is all about, we have to pop the hood and look at your body's energy engine. Think of your muscles as running on tiny, rechargeable batteries. Every single time you lift a weight, jump, or go for a sprint, you're draining those batteries to get the job done.
These microscopic batteries are called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), and they're the direct fuel source for every muscle contraction. But here’s the catch—your body only keeps enough ATP on hand for a few seconds of intense, all-out effort. Once that initial charge is spent, your performance takes a nosedive.
This is exactly where creatine comes in to save the day. It acts like a super-fast charging station, making sure those ATP batteries get juiced back up almost instantly so you can keep pushing hard.
The Power of the Phosphocreatine System
When your body uses ATP for energy, it loses a phosphate group and turns into ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate)—think of it as a dead battery. ADP is useless for power. To get back in the game, it needs to find that lost phosphate and become ATP again.
This is where your body’s creatine stores come into play. Most of the creatine in your muscles isn't just floating around; it's stored as phosphocreatine, which is just creatine holding onto a phosphate molecule.
When ATP gets used up and becomes ADP, the phosphocreatine system kicks into high gear. Phosphocreatine generously donates its phosphate molecule to the drained ADP, rapidly turning it back into high-energy ATP. This whole swap happens in a fraction of a second, giving your muscles an immediate refuel.
The phosphocreatine system is your body’s express lane for producing energy. It’s what lets you sustain maximum effort for longer, which translates directly to more reps in the gym or that extra burst of power on the field.
Taking a creatine monohydrate supplement is all about packing your muscles with more phosphocreatine. With a bigger stockpile of this rapid-recharge fuel, you can regenerate ATP way faster and more consistently than your body could on its own.
The process below shows you exactly how adding more creatine boosts your power output.
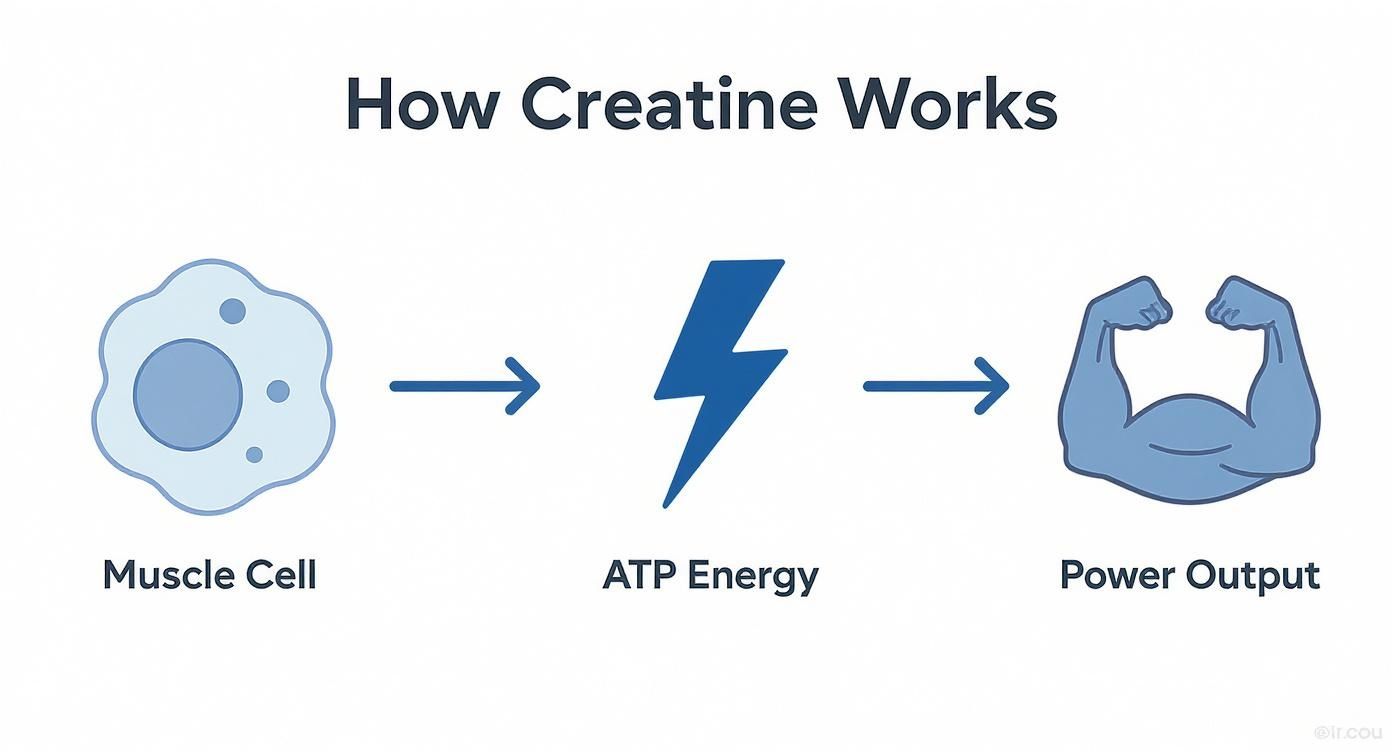
It’s a simple but powerful flow: more creatine in your muscle cells means faster ATP regeneration, which results in greater physical power.
Translating Science into Real-World Gains
So, what does all this cellular chemistry actually feel like during a workout? It’s the difference between hitting a wall on your eighth rep and pushing through for a ninth and tenth. It's that extra gear you find in the last few seconds of a sprint when you thought you had nothing left.
By keeping your ATP levels topped off, creatine gives you a real, tangible edge:
- Increased Strength and Power: With more instant energy available, you can lift heavier and generate more explosive force.
- Enhanced Muscular Endurance: You can simply do more work before feeling gassed, which means higher-volume training sessions—a key driver for muscle growth.
- Faster Recovery Between Sets: By quickly refilling your energy tank, you’re ready for the next set sooner, helping you keep the intensity high from start to finish.
This isn't just a cool theory; it's a proven physiological process backed by decades of solid research. In fact, over 90% of the creatine in your body is stored right in your muscle tissue, primed and ready to go. To dig even deeper into its effects, you can learn more about what creatine does to boost both physical and even cognitive performance.
Ultimately, understanding how it works shows you why creatine monohydrate has stood the test of time. It’s not magic—it's a supplement that works with your body's natural energy pathways to help you see real, measurable progress.
What Are the Real-World Benefits of Creatine?

It's one thing to understand the science of how creatine works inside your cells, but what really matters is how that translates to tangible results in the gym and on the field. The good news is that the benefits of creatine monohydrate aren't just theoretical—they're backed by a mountain of research, making it one of the most proven supplements you can buy.
These aren't just about looking better in the mirror, either. The advantages touch every part of physical performance, from pure, raw power to muscular endurance and even how sharp your brain feels. It's this widespread recognition that has fueled its incredible growth.
In fact, the global creatine supplement market was valued at $1.11 billion in 2024 and is on track to hit $4.21 billion by 2030. That boom reflects a massive public awakening to its effects on strength and recovery, with the classic powder form still holding a dominant 80.6% market share. You can read the full research about creatine market trends on Grandviewresearch.com for a deeper dive.
Enhanced Strength and Raw Power
The most famous benefit of creatine monohydrate is its immediate impact on strength and power. By helping your body regenerate ATP at lightning speed, it gives you the fuel to generate more force during those quick, explosive movements. This isn't some tiny, barely-there effect; it’s a measurable boost in what you can actually lift.
Think about your big lifts: the bench press, squat, or deadlift. Supplementing with creatine can be the difference between hitting a wall on your last rep and blasting right through it. Over time, that ability to consistently lift heavier is the single biggest key to unlocking long-term strength gains.
This is especially huge for any activity demanding short, intense bursts of effort:
- Weightlifting and Powerlifting: Directly improves your one-rep max potential and overall brute force.
- Sprinting: Gives you that explosive start and helps you hold your top speed for longer.
- Team Sports: A game-changer in sports like football or basketball, which are all about repeated, powerful movements.
It really is that simple: more available energy means more power.
Accelerated Muscle Growth
For anyone looking to pack on muscle (a process known as hypertrophy), creatine is a powerful ally. It doesn't just work in one way; it creates the perfect storm for muscle growth through several different mechanisms.
First and foremost, by making you stronger, creatine allows you to create a bigger stimulus for growth. Pushing heavier weights for more reps is the most direct signal you can send to your body to build more muscle tissue.
Creatine also pulls more water into your muscle cells. This process, called cell volumization, doesn't just give you a fuller, more "pumped" look. It’s also thought to kick off anabolic (muscle-building) signals that ramp up protein synthesis and slow down muscle breakdown.
On top of that, some research suggests creatine can positively influence hormones tied to muscle growth and even lower levels of myostatin—a protein notorious for putting the brakes on muscle development. This multi-pronged attack makes it a foundational supplement for building lean mass.
Improved High-Intensity Performance
Beyond just max strength on a single lift, creatine drastically improves your ability to perform repeated bouts of high-intensity exercise. This is where its role in rapidly refueling ATP really shines.
Picture yourself in the middle of a tough set of high-rep squats or a grueling HIIT session. Your ability to recover between those efforts dictates the quality of the entire workout. Creatine helps you bounce back faster, so you can maintain a higher level of performance from the first rep all the way to the last.
This translates into some very real-world advantages:
- Better Work Capacity: You can simply do more total work in a given training session.
- Reduced Fatigue: You'll find that exhaustion doesn't set in as quickly, letting you push harder for longer.
- Faster Recovery Between Sets: You feel ready for that next set sooner, which helps keep your workout intensity high.
For athletes and serious gym-goers, this means more productive training sessions, which ultimately leads to faster, more impressive results.
Emerging Cognitive Benefits
While it built its reputation in the gym, one of the most exciting new frontiers for creatine research is its effect on the brain. Just like your muscles, your brain is an energy-hungry organ that guzzles ATP to function at its best.
By making more energy available to your brain cells, creatine supplementation has been shown to support cognitive function, especially when you're under stress or tackling mentally draining tasks.
Early studies are pointing to some exciting potential mental perks:
- Improved Short-Term Memory: This seems especially true in demanding situations, like during periods of stress or sleep deprivation.
- Enhanced Mental Processing Speed: The ability to think and reason a little bit faster.
- Reduced Mental Fatigue: Helping you stay sharp and focused during long workdays or study sessions.
While more research is still needed, these findings suggest that the benefits of creatine monohydrate go far beyond the weight room, potentially supporting brain health and everyday mental performance. It's a truly versatile supplement for both body and mind.
Using Creatine Monohydrate for Maximum Results

Knowing how creatine works is one thing, but making it work for you is what really matters. Getting the most out of it comes down to a few simple, time-tested strategies. The good news? You don’t need some complex, color-coded spreadsheet to unlock its potential.
There are really two main ways people go about it: a "loading phase" or just jumping straight into a "maintenance phase." The only difference is how fast you fill up your muscles' creatine stores. Both roads lead to the same destination, so your choice just depends on whether you're in a hurry to feel the initial effects.
The Optional Loading Phase
A loading phase is all about speed. Think of it as quickly topping off your gas tank instead of letting it fill up drip by drip. The idea is to take a higher dose for a short burst to saturate your muscles as fast as possible.
Here's the classic approach:
- Dosage: Take 20 grams of creatine monohydrate per day.
- Duration: Stick with this for 5–7 days.
- Frequency: Don't chug all 20 grams at once. Split it into four 5-gram servings throughout the day to make it easier on your stomach and improve absorption.
After that first week, you’d drop back to a standard maintenance dose. While it definitely works, this loading method is completely optional. You'll get to the exact same saturation point by just taking a consistent maintenance dose—it’ll just take about three or four weeks.
The Simple Maintenance Phase
This is the most common, straightforward, and sustainable approach. A maintenance phase is exactly what it sounds like: taking a small, consistent amount every day to keep your creatine levels maxed out.
For most people, a daily dose of 3–5 grams is the gold standard. This amount has been proven time and again in scientific studies to keep muscle creatine stores full, ensuring you get those consistent benefits for strength, power, and recovery.
This no-fuss method is perfect for anyone who values simplicity. Just take your daily serving, and you're done. No need to juggle multiple doses or adjust your intake after a week. If you want to dive deeper into dosing strategies, our comprehensive creatine dosage guide breaks it all down.
Timing and Hydration Are Key
So, when’s the best time to take creatine? The honest answer is that consistency is far more important than timing. The whole goal is to keep your muscles saturated, so taking it at roughly the same time every day is what really counts, whether that's with your morning coffee or your post-workout shake.
Some research hints that taking it after a workout with some carbs and protein might give you a slight edge in absorption, but the difference is pretty small. The single most important factor is just remembering to take it.
Just as crucial is your water intake. Creatine pulls water into your muscle cells—that's a key part of how it works its magic. To help it do its job and keep yourself feeling good, make sure you're drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Choosing the Right Form for You
Creatine monohydrate comes in a few different forms, but powders and gummies are the most popular by far. Powder has been the king for a long time, holding a 39.3% market share in 2024, which is valued at $202.5 million. This market is only expected to grow as everyone from pro athletes to older adults recognizes its value for maintaining muscle.
Here’s a quick rundown of your main options:
- Powders: The traditional choice. They're usually cheap, but let's be honest—they can be messy. Scooping and mixing isn't always convenient, especially when you're on the go.
- Gummies: A modern solution like Smash creatine gummies offers a pre-measured dose in a form that's easy (and tasty) to take. They completely remove the hassle of powders, making it effortless to stay consistent.
To really get the best results, it helps to see how supplements fit into a bigger picture. For more on this, it's worth exploring the interplay between exercise and supplement use. At the end of the day, the best form of creatine is the one you’ll actually take every single day.
Common Myths and Safety Concerns Addressed
Creatine is one of the most studied supplements on the planet, yet it's still dogged by myths and outdated fears. These persistent misunderstandings can make people nervous, but when you dig into the actual science, a very different picture emerges. Let's cut through the noise and tackle these common concerns head-on.
There's a reason creatine is everywhere—it works. Creatine monohydrate is by far the most researched form, and its proven results and affordability have made it a staple in sports nutrition. In fact, the global market for its raw material was valued at around $427 million back in 2025, which shows just how foundational it is. This demand comes straight from athletes and everyday gym-goers who want a reliable edge. You can see the numbers for yourself in the creatine monohydrate market trends on Archivemarketresearch.com.
Now, let's get into the myths.
Myth 1: It Damages Your Kidneys
This is probably the biggest and most persistent myth out there, but it’s built on a simple misunderstanding. The worry comes from the fact that taking creatine can slightly raise blood levels of creatinine, a waste product that doctors use as a marker for kidney function.
But here’s the key: this small bump isn't a sign of kidney damage. It’s just a harmless and expected byproduct of breaking down the extra creatine you're taking.
Countless long-term studies on healthy people have shown no evidence that creatine supplementation harms the kidneys. Major sports nutrition and scientific bodies have all come to the same conclusion: at recommended doses, creatine has an excellent safety profile. For anyone with healthy kidneys, it’s perfectly safe.
The idea that creatine is harmful to the kidneys is a classic case of confusing correlation with causation. The slight rise in creatinine levels is an expected and benign outcome of supplementation, not an indicator of renal stress.
Of course, if you have a pre-existing kidney condition, you should always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on whether creatine damages kidneys.
Myth 2: It Causes Dehydration and Cramping
Another common myth is that creatine "steals" water from the rest of your body, leading to dehydration and muscle cramps. This idea comes from a misinterpretation of how creatine actually works. Yes, it draws water into your muscle cells—a process called cell volumization—but this is actually a good thing.
This extra water inside the muscle tissue helps keep it hydrated, which can boost performance and even support muscle growth. Study after study has failed to find any link between creatine use and an increased risk of cramping or dehydration. If anything, some research suggests it might help athletes better handle the heat and lower their risk of heat-related illnesses.
Staying hydrated is always important, especially when you're training hard, but creatine isn't going to put you at any special risk.
Myth 3: It Is a Steroid
Let’s be crystal clear: this is completely false. Creatine monohydrate is not an anabolic steroid or any other kind of performance-enhancing drug. It's a natural compound your body already produces from amino acids and gets from food like red meat and fish.
The two aren't even in the same universe.
- How They Work: Creatine works by supercharging your body’s natural energy (ATP) production. Steroids are synthetic hormones that directly manipulate your body's testosterone levels.
- Legality: Creatine is a legal, over-the-counter supplement that's allowed by every major sports organization.
- Chemistry: Their chemical structures are fundamentally different.
Comparing creatine to a steroid is like comparing vitamin C to a prescription antibiotic. One enhances your body's natural systems, while the other artificially alters your hormones. They simply aren't the same.
Got Questions About Creatine? We've Got Answers.
Even after digging into the science, benefits, and best practices, a few questions always seem to pop up. This is where we tackle those lingering "what ifs" and practical, day-to-day concerns about creatine monohydrate. Think of this as your final checklist before you get started.
Let's clear up the common sticking points so you can move forward with total confidence.
Do I Really Need to Cycle Creatine?
This is probably one of the most persistent myths out there, and thankfully, the answer is simple. No, you do not need to cycle creatine monohydrate.
The whole idea of "cycling"—taking something for a while, then stopping—comes from other supplements where your body might build a tolerance or where the long-term safety wasn't as well-established. Creatine just isn't in that category. Your body doesn't get "used to it" in a way that makes it less effective.
The entire goal is to keep your muscle creatine stores topped off. The modern, science-backed way to do that is through consistent, daily supplementation. A simple 3–5 gram daily dose keeps your muscles fueled and ready to perform.
Stopping your intake just lets your creatine levels slowly drift back down to your baseline, which temporarily wipes out the benefits. There's no physiological advantage to starting and stopping. In fact, it's counterproductive because you have to spend time re-saturating your muscles every time you start a new cycle. Just stick with a daily dose—it’s easier, more effective, and backed by a mountain of safety research.
Is Creatine a Good Supplement for Women?
Absolutely. The old-school myth that creatine is just for male bodybuilders or that it will make women "bulky" is completely outdated and has been thoroughly debunked by science. The benefits of creatine—more strength, better performance, faster recovery, and even a cognitive edge—are just as real and valuable for women.
That fear of unwanted bulk? It's a total misconception. Building significant muscle is a tough, slow process that demands a very specific kind of intense training paired with a serious calorie surplus. Creatine doesn't magically create bulk on its own.
Here’s what it actually does for women:
- Improves Strength: Helps you push heavier weights and get more out of every single rep in your workouts.
- Enhances Muscle Tone: By supporting the development of lean muscle, it helps create that toned, athletic look many people are after.
- Boosts Workout Performance: Lets you go harder for longer during HIIT, sprints, or any other all-out effort.
- Supports Brain Health: The cognitive benefits are for everyone, helping with focus and mental clarity.
Any initial weight you might notice is simply water being pulled into your muscle cells—which is a good sign that the creatine is working! This "intracellular" water actually helps muscles look fuller and more defined, not soft or bloated. For any woman looking to level up her fitness, creatine is one of the safest and most powerful tools you can have in your corner.
What Happens If I Stop Taking It?
If you decide to stop taking creatine, don't worry—there's no dramatic crash or sudden loss of all your hard-earned gains. The process is actually pretty gradual and predictable.
Over about 3 to 4 weeks, your body will slowly flush out the extra creatine, and your muscle stores will return to their normal, pre-supplementation levels.
As this happens, you’ll probably notice a few subtle shifts:
- A slight dip in strength and power: You might find it a bit harder to squeeze out that last extra rep you could when your stores were full.
- A little less endurance: You may feel gassed a bit sooner during those really intense sets.
- A loss of a few pounds: This is just the extra water leaving your muscles, not a loss of actual muscle tissue.
Your muscles won't just vanish. All the real strength and lean tissue you built in the gym is yours to keep. You’ll just be operating without that extra performance edge that fully saturated creatine stores provide. The best part? You can always start taking it again, and you'll be right back at peak levels within a few weeks.
Ready to skip the messy powders and chalky drinks for good? Smash.com makes staying consistent with your creatine completely effortless. Our delicious, pre-dosed creatine gummies deliver the full 5-gram serving you need to fuel your goals, anytime and anywhere.