
Does Creatine Make You Bigger? The Real Science
Share
Let's get straight to it: Yes, creatine makes you bigger. But how it does so is a two-part story. First comes a rapid increase in size from water, which then sets the stage for genuine, hard-earned muscle growth over time.
The Straight Answer on Creatine and Gaining Size
Anyone who's been around a gym has heard the question: "Is the size from creatine just water weight?" The honest answer is that it starts that way, but it doesn't end there.
Think of it like this: creatine acts as a magnet for water, but it pulls that water inside your muscle cells, not under your skin. This process, known as cell volumization, is what gives your muscles that full, dense look pretty quickly after you start taking it. This isn't the same as the subcutaneous bloating you might get from a salty meal; this is functional hydration that creates an optimal environment for growth.
That initial pump and fullness is the first sign that the creatine is doing its job. It's laying the groundwork for real, lasting muscle.
Water vs. Muscle: A Two-Phase Process
The journey to getting bigger with creatine happens in two distinct phases. The first is that quick, motivating size increase from water, which you can often see and feel within the first week.
But the real magic happens over the long haul. Creatine’s primary benefit is boosting your performance. It helps your muscles generate energy more rapidly, allowing you to push out that extra rep or add another 5 lbs to the bar. This enhanced workload is the direct signal your body needs to start building new muscle tissue.
The key takeaway is that the initial water gain is a catalyst. It supports the main event: permanent muscle growth fueled by your improved performance in the gym.
This visual gives you a great snapshot of what to expect from creatine supplementation over time.
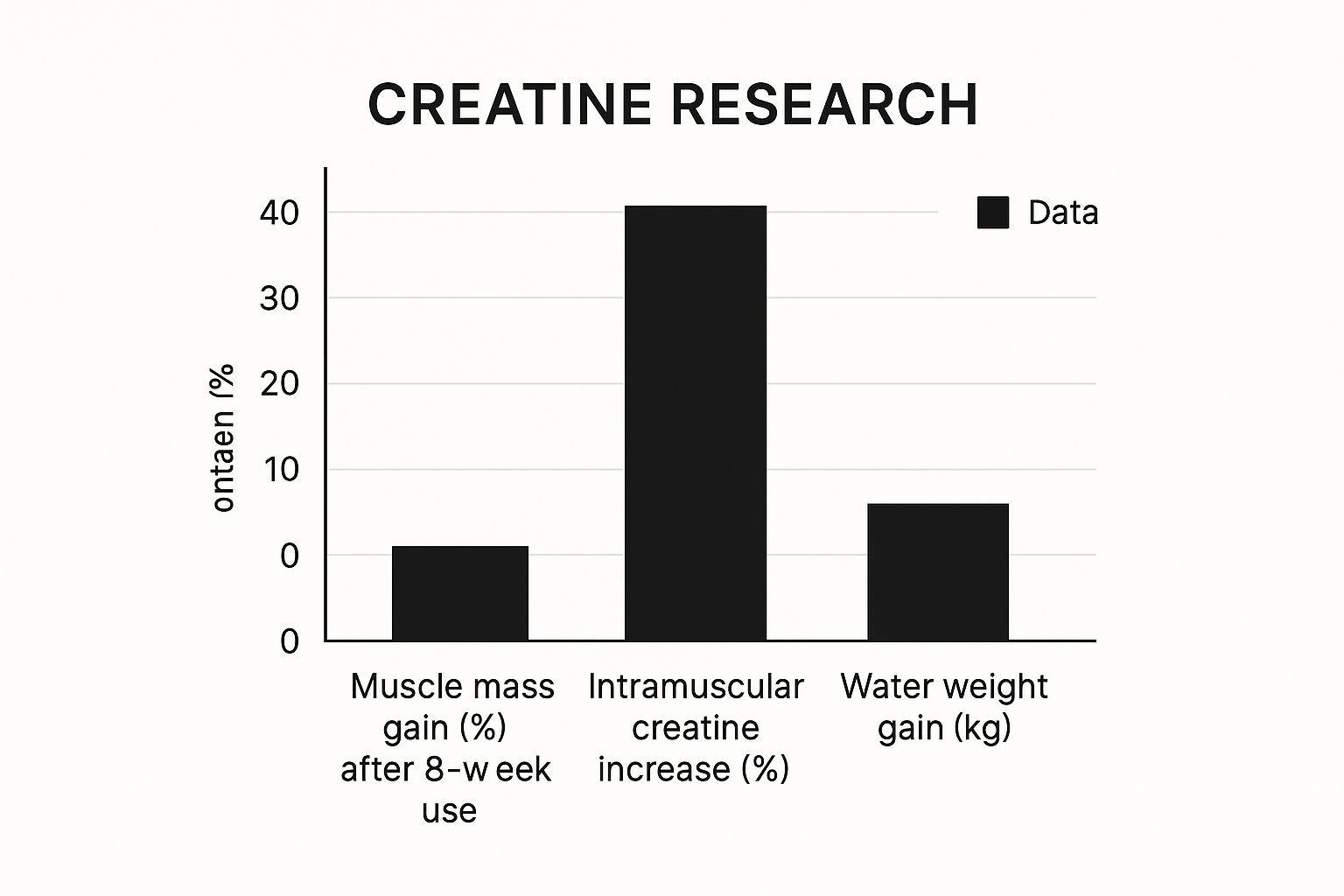
As you can see, the initial spike in water weight happens right alongside the rise in intramuscular creatine levels. More importantly, this is followed by a steady, sustained increase in actual muscle mass.
To give you a clearer picture, let's break down these two effects side-by-side.
How Creatine Adds Size At a Glance
| Effect | What It Is | How It Happens | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Cell Volumization | Rapid increase in muscle fullness due to water. | Creatine pulls water directly into muscle cells, hydrating and expanding them. | First 1-2 weeks |
| Phase 2: True Hypertrophy | Gradual growth of actual muscle fiber. | Improved workout performance (more reps/weight) stimulates new muscle synthesis. | Begins after a few weeks; ongoing with consistent training. |
This two-step process isn't just gym lore; it's backed by solid science.
The evidence is overwhelming. Creatine is one of the most studied supplements on the planet, and study after study has shown it significantly increases muscle mass when combined with resistance training. A massive 2022 review that looked at 35 different studies confirmed that creatine supplementation delivers major boosts in muscle strength, performance, and hypertrophy (muscle growth) when compared to a placebo.
If you want to dive into the data yourself, you can explore the full research on creatine and hypertrophy and see why it’s a trusted staple for anyone serious about gaining size and strength.
How Creatine Fuels Real Muscle Growth

While that initial water gain is a nice bonus, it's not the main event. The real magic of creatine lies in how it directly fuels your performance in the gym. It fundamentally alters how your muscles generate energy during those short, explosive efforts, like a heavy set of squats or a full-out sprint.
Think of your muscle cells as tiny engines that run on a high-octane fuel called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This is your body’s go-to energy source for immediate, powerful movements. The catch? You only have a tiny reserve tank—enough for just a few seconds of all-out effort before you're running on fumes.
This is where creatine comes in to save the day. It acts like a super-fast recharging station for your cellular batteries.
Supercharging Your Cellular Engine
When you take creatine, you’re stocking up your body's supply of phosphocreatine, which is basically energy stored on standby. During a tough set, once you’ve burned through your initial ATP, this phosphocreatine steps in, quickly donating a phosphate molecule to regenerate ATP on the fly.
This rapid recycling process means you can push harder for longer. That set where you usually hit a wall at eight reps? You might suddenly have the juice to grind out ten or even eleven.
In simple terms, creatine doesn't build muscle directly. It gives you the ability to do the hard work that is the direct trigger for muscle growth. More work equals more growth.
That extra work you're now able to do—those additional reps, that slightly heavier weight—is the single most important signal you can send your body to adapt and grow stronger. By boosting your total training volume, you create a far more powerful stimulus for muscle protein synthesis, which is the biological process of repairing and building bigger, stronger muscle fibers.
The Anabolic Signaling Cascade
But there's more to the story. Beyond just providing extra fuel, creatine also talks to your cells and kicks off a chain reaction of muscle-building events. That initial cell swelling from the water retention isn't just for show; it actually helps trigger a cascade of anabolic (muscle-building) signals.
This process unlocks several key benefits that work together to pack on size:
- Increased Workload: This is the big one we've covered. It lets you lift heavier and for more reps, which is the cornerstone of hypertrophy.
- Improved Anabolic Signaling: Creatine helps fire up crucial pathways like mTOR, which are like the master switches for turning on muscle protein synthesis.
- Reduced Muscle Breakdown: Some research suggests creatine can help lower levels of myostatin, a protein that actively puts the brakes on muscle growth. Less braking means more building.
By stacking these effects, creatine delivers a powerful one-two punch. It helps you crush your workouts and simultaneously primes your body’s internal environment to capitalize on that hard work. To get an even deeper look at the science, you can explore our detailed guide on using creatine for muscle growth and see how these mechanisms translate to real-world gains.
Ultimately, creatine isn’t a magic pill. It’s a tool that amplifies the results you earn. It gives you the capacity to train harder and more effectively, and that consistent, progressive overload is what truly answers the question "does creatine make you bigger" with a definitive yes.
Decoding the Water Weight Myth

Let's tackle one of the oldest, most persistent myths about creatine: that it just makes you bloated and puffy. I hear it all the time—the idea that any size you gain is "just water weight," and it's enough to scare some people away. But this comes from a fundamental misunderstanding of where that water goes and what it’s actually doing.
When you start taking creatine, your body stores it in your muscles. Because of its chemical properties, creatine molecules pull water into the muscle along with them. This process is called intracellular hydration, which is a fancy way of saying the water is drawn directly into your muscle cells.
This is the critical detail most people miss. The water isn't just sitting under your skin, blurring your definition and making you look soft. That’s a completely different kind of water retention. Instead, creatine is making your muscle cells themselves fuller, denser, and more voluminous from the inside out.
A Good Kind of Swelling
Think of your muscle like a flat tire. Before you add air, it's limp and useless. As you pump it up, it becomes firm, round, and ready to perform. The water creatine pulls into your muscles does something very similar, leading to that hard, "pumped" look and feel.
This cell swelling—or volumization—is actually a huge positive. Your body interprets this expansion as a signal of stress, a trigger that tells the muscle it needs to adapt and grow stronger. It literally creates a pro-muscle-building (anabolic) environment right where you need it most.
That initial water gain from creatine isn't a side effect you should try to avoid. It’s one of its primary mechanisms of action. It's the proof that the supplement is working and setting the stage for real muscle growth.
This immediate increase in cell volume is the first visible answer to the question "does creatine make you bigger?" It’s the opening act for the main event: enhanced strength and performance.
Intracellular vs. Subcutaneous Water
To make it crystal clear, not all water retention is created equal. Understanding the difference is everything when it comes to building a better physique.
Here's a quick rundown of the two types of water you'll hear about:
- Intracellular Water (The Good Stuff): This is the water stored inside your muscle cells. It’s what gives you a full, hard, and vascular appearance. This is the type of hydration creatine promotes.
- Subcutaneous Water (The Bad Stuff): This is the water held outside the muscle cells, just beneath the skin. It’s what blurs muscle definition and can give you a puffy look, often caused by a high-sodium diet or hormonal shifts.
Creatine specifically increases intracellular water, which directly contributes to muscle size and primes the pump for hypertrophy (actual muscle fiber growth). This initial hydration isn't just a temporary boost; it’s the foundational step that supports the strength gains and real muscle you'll build with consistent training. It’s not just water—it’s smart water, put to work exactly where you want it.
Setting Realistic Expectations for Size and Strength
So, let's get down to it. Does creatine actually make you bigger? We already know the answer is yes, but it’s time to move past the marketing hype and talk about what you can realistically expect. Forgetting the promises of overnight transformations is the first step to using creatine as a smart, sustainable tool for long-term progress.
Think of creatine as a performance enhancer for your training, not a magic pill. The size and strength you gain come directly from the extra work it empowers you to do in the gym. This is all built on the foundation of your diet, how consistently you train, and even your genetics. It’s like adding a turbocharger to your car’s engine—it definitely makes it more powerful, but you still have to be a good driver to win the race.
The first thing you’ll notice is a bit of size from extra water, which gives your muscles a fuller look within the first couple of weeks. But the real goal—actual muscle growth, or true hypertrophy—is a much slower and steadier process.
What the Science Says About Gains
When we dig into the research, a clear picture starts to form. Study after study shows that people who combine creatine with resistance training consistently gain more lean muscle and strength than those who don't. But what does that look like in real numbers?
A major 2023 meta-analysis pulled together the results from 10 high-quality studies to get a definitive answer. It found that creatine use led to a small but statistically significant boost in muscle thickness. After several weeks of hard training, the creatine groups saw gains of 0.10 to 0.16 cm more than the placebo groups in both their upper and lower body muscles. You can learn more about these muscle thickness findings if you want to see the direct data for yourself.
Now, that might not sound like a massive jump, but in the world of building muscle, it's a very real edge that adds up over months and years of consistent effort.
These numbers prove that creatine offers a real, quantifiable boost. It’s a marathon, not a sprint—a tool that helps you consistently lay one brick at a time, not one that builds the entire house overnight.
Factors That Influence Your Results
It's really important to remember that these are just averages. Your personal results will swing based on a few key things:
- Training Intensity: You have to give the creatine something to work with. If you aren't pushing yourself and challenging your muscles in the gym, you simply won't trigger the growth you're looking for.
- Diet and Nutrition: Muscle doesn't just appear out of nowhere. A diet rich in protein is non-negotiable for repairing muscle damage and building new tissue. In fact, combining creatine with enough protein is critical, as they work as a team to support hypertrophy. You can read our guide on taking creatine and protein together to really dial in your strategy.
- Genetics: Let's be honest—some people are just "high responders" who build muscle and react to creatine incredibly well. Others might see more modest, but still valuable, gains.
At the end of the day, managing your expectations is the key to success. Creatine will absolutely help you get bigger and stronger, but those results are earned through your dedication, not just by taking a supplement. It gives you the power to squeeze out one more rep, lift a little heavier, and recover just a bit faster—and that is what truly builds a stronger, bigger physique in the long run.
Your Practical Guide to Using Creatine Effectively
 Alright, now that you know the science behind how creatine helps you get bigger, let's talk about putting it to work. Building a solid plan is surprisingly simple. Forget complicated protocols—the real secret to getting results is consistency and picking the right strategy for your body and goals.
Alright, now that you know the science behind how creatine helps you get bigger, let's talk about putting it to work. Building a solid plan is surprisingly simple. Forget complicated protocols—the real secret to getting results is consistency and picking the right strategy for your body and goals.
When it comes to starting creatine, there are really two main camps: the "loading phase" and the straight "maintenance dose."
The loading phase is the fast track. The idea is to saturate your muscles with creatine as quickly as possible by taking a higher dose—typically 20-25 grams per day—for about 5-7 days. To make it easier on your stomach and improve absorption, you'd split this into 4-5 smaller doses throughout the day. After that first week, you drop down to a regular daily maintenance dose.
The appeal of loading is speed. You'll fill up your muscle stores much faster and probably feel the performance benefits a week or two earlier. But here's the thing: it's not a requirement.
Choosing Your Dosing Strategy
The other method, which is often much simpler, is to just skip the loading phase altogether. You can jump right in with a standard maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day. It will take a bit longer to reach full muscle saturation—usually around 3-4 weeks—but you'll get to the exact same place in the end.
This approach is gentler on your system and honestly, just easier to stick with. For most people, it's the perfect way to go. If you want to dive deeper into nailing down your exact daily amount, check out our complete creatine dosage guide from beginner to expert.
To help you decide, here’s a quick breakdown:
| Dosing Method | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loading Phase | Saturates muscles faster for quicker results. | Higher initial dose might cause digestive upset for some. | Athletes prepping for a competition or anyone who wants the fastest benefits possible. |
| Maintenance Dose | Simpler, easier to maintain, and less likely to cause side effects. | Takes about 3-4 weeks to reach full muscle saturation. | Most people who are in it for sustainable, long-term muscle and strength gains. |
Ultimately, both paths lead to the same destination. Your choice really just boils down to how fast you want to get there.
The Great Timing Debate: Pre vs. Post-Workout
So, what about timing? You'll hear people swear by taking creatine before a workout for an instant boost, while others insist that post-workout is the only way to go for recovery. While the debate is passionate, the science is pretty clear: consistency is king.
Taking your creatine daily is worlds more important than the exact minute you take it. The entire goal is to keep your muscle creatine stores topped off, and that only happens with a steady, daily habit.
The most important rule of creatine is to simply take it every single day. Whether it's with your morning smoothie, your post-workout shake, or your dinner, consistency will always beat perfect timing.
With that said, there is some research that points to a slight edge for taking it post-workout. One study found that people taking creatine after their training saw a slightly greater increase in lean mass than the pre-workout group. For instance, the post-exercise group saw their lean mass jump from an average of 46.6 kg to 49.6 kg. The difference was small, but it was there—and both groups made significant progress.
The bottom line is simple: find a time that fits your routine so well that you never miss a day. That simple habit is what unlocks creatine's true power to help you get bigger and stronger.
Common Questions About Creatine and Size
Even with all the science laid out, a few practical questions always pop up when you're thinking about adding creatine to your routine. Let's tackle these head-on. Clearing up these common doubts is the best way to feel confident you're making the right move for your goals.
My goal here is to give you straight-up, no-nonsense answers, so you know exactly what to expect when you start, while you're taking it, and even if you decide to stop.
Will I Lose My Gains If I Stop Taking Creatine?
This is easily the biggest fear people have, and I get it. But the good news is, it's mostly a myth. The short answer is no, you won’t lose the actual muscle you busted your butt in the gym to build.
Here’s what really happens. When you stop taking creatine, your body’s stores will slowly drift back down to their normal baseline over a few weeks. As they do, the extra water that was pulled into your muscle cells gets flushed out. You'll probably notice your muscles look a little less "full," and the number on the scale might dip by a few pounds.
But it's critical to understand what you're not losing. The actual muscle fibers you built through consistent training and solid nutrition? They’re yours to keep. The strength you gained is real, too, though you might find it a touch harder to grind out that last punishing rep without the extra ATP energy. As long as you keep training hard and eating right, your true gains are safe.
Does Creatine Work for Everybody?
For the vast majority of people, creatine is a game-changer. That said, results can vary. A small slice of the population are considered "non-responders," meaning they don't experience a noticeable performance boost from it.
This isn't because the supplement is faulty or something is wrong with them. It’s usually because their baseline creatine levels are already naturally high. This is most common in people who eat a diet packed with red meat and fish, which are fantastic natural sources of creatine. In simple terms, their tank is already full from their diet.
On the other end of the spectrum, vegetarians and vegans often see the most dramatic results. Because their diets provide very little to no creatine, their baseline levels are much lower. Supplementing gives them a massive boost, letting their muscles get fully saturated for the very first time.
Your personal response to creatine has more to do with your unique physiology and diet than it does with your body type or how long you've been training. For most of us, consistent use paired with dedicated training will absolutely deliver results you can see and feel.
Are There Any Side Effects Besides Gaining Size?
Creatine is one of the most heavily researched sports supplements on the planet, and its safety record is stellar. The main "side effect"—and the one we're all looking for—is gaining size from both new muscle tissue and that helpful intracellular water.
Beyond that, negative side effects are minimal and pretty rare. Some people mention minor stomach discomfort, like bloating, but this is almost always tied to taking a massive dose all at once, especially during an aggressive loading phase. This is easily sidestepped:
- Skip the load: Just start with a simple 3-5 gram maintenance dose from day one. It’s just as effective over the long haul.
- Split the dose: If you do want to load, break it up into smaller 5-gram servings spread throughout the day.
- Take it with food: Having your creatine with a meal can help prevent any potential stomach issues.
Staying properly hydrated is also key. Since creatine is actively pulling water into your muscles, you need to make sure you're drinking enough to support that process and the rest of your body’s needs. And as with any new supplement, if you have a pre-existing health condition (especially related to your kidneys), it's always smart to have a quick chat with your doctor first.
Ready to experience the muscle-building benefits without the messy powders and chalky taste? Smash.com makes staying consistent effortless with our delicious creatine gummies. Each serving delivers the full 5g of pure creatine you need to fuel your workouts, boost your strength, and build the size you've been working for. Try Smash.com creatine gummies today and make your daily dose the best part of your routine.